1. Operating system
An operating system is a system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and that provides common services for computer programs running on a device. The operating system thus serves as an intermediary that determines how the person programming an IoT device can take advantage of the sensors, memory, computing, networking, and other resources that are available on the device.
IOT devices can have or not have OS.
With no OS devices, programs require low level code to interact directly with HW
With OS devices, we have 3 choices
+ Low-end OS: run on resource-constrained devices, provide essential functions, lack GUI. Example: firmware
+ Embedded OS: tailored to a devices that run specific set of applications. For example: QNX, Ubuntu
+ Smart OS: run in feature rich devices such as smart phone, TV …
2. Sensor
Sensors has several characteristics:
A sensor should be sensitive to the property they are measuring.
A sensor should be insensitive to other properties encountered in its application domain.
A sensor should have no influence on the property it is measuring.
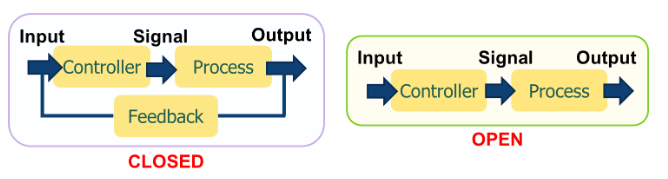
Control system can be classified as open loop and close loop
A sensor has sampling rate and it should be twice the rate of the behavior we are sampling.
The quality of sensors is characterized by Precise and Accurate.
Sensor errors include bias, drift, cross sensitivity and context dependency.
There are 3 main ways to read a sensor
Streaming: the interface to the sensor is open and measurements are read continuously.
Polling: the sensor interface is periodically queried for measurements.
Event-Based: The sensors inform the operating system whenever new measurements are available
The process to orchestrate data flow of sensor with machine learning is called sensing pipeline
if you like my ideas, hit button 💙
If you have any feedback, make sure to 💬 comment.
If you find this helpful, let’s 🔁 share it.